Your hospitalization
Different consults will systematically be set-up before the operation:
- A pre-surgery consultation: clinical exam, choosing the operation day, the location of the battery;
- An anesthesia consult:
- A pre-operation EPT (educational physical therapy) session.
The intervention
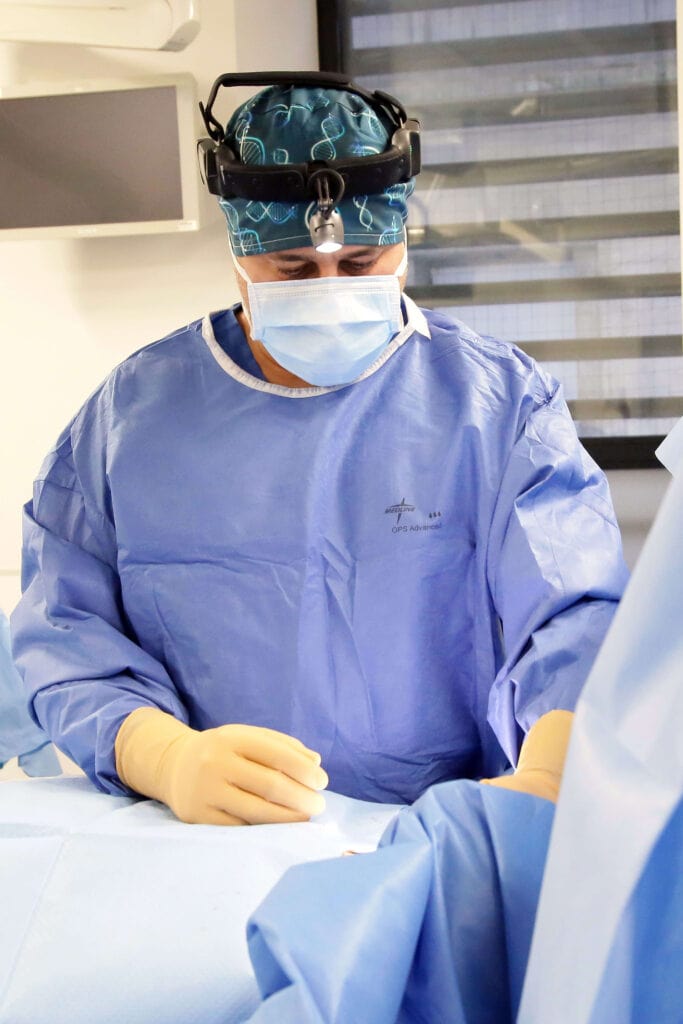
The intervention takes place in 3 steps:
- 1. Identifying the target-areas
- 2. Placing the leads
- 3. Placing the stimulation generator
Identifying the target-areas
A brain MRI in stereotactic conditions takes place, eventually in addition to a cerebral CT scan. A stereotaxic frame is, while under local anesthesia, secured on the skull. That metal piece is made up of a rigid bottom and four vertical props who allow the identification of the target cerebral area, in both great precision and in the three dimensions of space.
Placing the trial leads
You are then moved once more into the operating room so that the electrodes can be implanted, under either local or general anesthesia. Testing micro-electrodes can be implanted to record the neurons electrophysiological activity to begin with and refine the trajectory calculation.
If the patient is under local anesthesia, those micro-electrodes can be used to achieve electric stimulation on the target-area to test their impact of the illness’ symptoms. The testing micro-electrodes are then removed, and the permanent electrodes implanted instead.
Placing the stimulation generator
The lead is then (either at the same time or a few days later) connected to a neurostimulator which is generally implanted abdominally or in the area under the collarbone, through a subcutaneous connection cable. It is connected to the cerebral electrodes via subcutaneous extensions.